Origin and History of Manhattan
Origin of Manhattan
Manhattan (/ maenˈhaetən /) is the most densely populated and the smallest in the area of the five boroughs of New York. Located primarily on Manhattan island at the mouth of the Hudson River, the village is contiguous with New York County, an original County of New York State. The city and the county consists of Manhattan island and several small adjacent islands: Roosevelt Island, Randall Island, island of neighborhoods, Governors Island, liberty Island, part of Ellis Island, mill rock and U Thant island; as well as Marble Hill, a small area in the continent bordering the Bronx. The original in New York began in the southern tip of Manhattan, expanded northward and then between 1874-1898, annexes land from surrounding counties.New York County is the most densely populated County in the United States and one of the most densely populated areas in the world, with a population of 2010 of 1.585.873 living in an area of 22.96 square kilometers (59.5), or 69.464 people per square mile (26.924/km²), denser than any single American city. One of the richest in the United States counties, is also with a per capita income in 2005 de100.000 dollars. Manhattan is the third of five boroughs of New York in its smallest municipality in land area and population.
Manhattan is a commercial important, financial and cultural center of the United States. Anchored by Wall Street in functions of Lower Manhattan, in New York as the financial capital of the world, with an estimated GDP of more than $1.2 trillion. and it is home to the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ. Many large companies in radio, television and telecommunications in the United States have their headquarters here, as well as many news, magazine, book, and other media publishers.
Manhattan has many famous landmarks, tourist attractions, museums, and universities. It is also the location of the headquarters of the United Nations. It is the center of the city of New York and the New York metropolitan area, is home to the headquarters of the Government of the city and a large part of employment, business and entertainment in the area. As a result, the residents of the other districts in New York City as Brooklyn and Queens often referring to a trip to Manhattan as "going to the city", despite comparable populations between the municipalities and the fact that these municipalities are also considered part of the city.
New York City
A city of Islands, is made up of five boroughs: Manhattan island, Staten Island, Queens, Brooklyn and the Bronx, connected by tunnels and bridges. Many of the leading industrial companies in the nation have their headquarters in Manhattan of New York City. Wall Street is justly famous as a financial center in the world. It is the commercial and financial leader of the country as well as a major distribution center. Financial institutions, insurance companies and real estate contributes one third of the gross product of the State, followed by services, trade, and manufacturing. The port of New York, one of the biggest and best the world's natural hosts, handles much of the foreign trade of the United States. New York, with 1.7 million of their jobs, dominates the State employment. The metropolitan area of New York City, including parts of eight counties, has many industrial workers in the State and generates much of the State's industrial revenue. High-value printing and publication of the industry are strongly concentrated in the metropolitan area of the city of New York. The electrical and electronic industry is a unique source of manufacturing jobs in New York.
Railways play a particularly important role in the transport of passengers between New York and neighboring suburban areas. New York is crossed under the ground with the world most extensive metro system. J.F. Kennedy International Airport and La Guardia Airport giant of the city of New York are among the busiest in the world.
The city is also notable for its fusion of many cultures. People of all races, religions and ethnic groups are part of this cauldron of diversity. Head of New York religion is Roman Catholicism; The Protestants are the second group including Methodists and Baptists, followed by the Jews. More than one quarter of the Jews in the United States live in New York. The city is in the heart of the cultural life of the nation. Broadway is known worldwide for its theaters and offers a wide variety of musical and dramatic activities. So do the Lincoln Center for the performing arts, Carnegie Hall and the Brooklyn Academy of Music. Museums such as the Solomon r. Guggenheim Museum and the Metropolitan Museum of art are among the best in the world. Central Park in the heart of Manhattan is a legend in its own right. Also in New York City are the Federal Hall National Memorial, home of the first Congress of the United States; Castle Clinton National Monument, originally a strong but has served many purposes during the history of the nation; General Grant National Memorial, the tomb and displays about Ulyss
Names
The name Manhattan derives from the word manna-hata, as written in the book of 1609 of Robert Juet, an officer of Henry Hudson yacht half Maen (half moon).A 1610 map describes the name as manna-hata, twice, on the sides East and West of the Mauritius River (later named the Hudson River).The word "Manhattan" has been translated as "island of many hills" in the Lenape language.
New York County is one of the seven counties in the United States to share the same name as the State where they are (the other six counties are County of Arkansas, County of Hawaii, in Idaho, Iowa County, Oklahoma County and Utah County).
The United States Postal Service prefers that mail addressed to Manhattan use "New York" instead of "Manhattan, NY".
History
Colonial era
The area of Manhattan for a long time was inhabited by the Lenape Indians.In 1524, Italian Explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano - sailing in the service of the French King Francisco I - was the first European to visit the area that would become New York City.He entered The Narrows on Board of his ship La Dauphine and call of the earth around the Bay of New York upper "Angouleme", the name of the family of Francis I;sailed far enough into the port view of the Hudson River, who stated in his report to the French as "large river"; Kingand named the New York Bay the Bay of Santa Margarita - Margarita de Navarra - the older sister of the King.
Was not until the voyage of Henry Hudson, an Englishman who worked for the Dutch company of the East Indies, was assigned to the area.Hudson came across Manhattan island and the natives who live in 1609, and continued up the river that would later take his name, the Hudson River, until he arrived at the site of the current Albany.
The Castello Plan showing the Dutch colonial city of new Amsterdam in 1660 - then confined to the southern tip of the island of Manhattan.
Overview of eye of Manhattan bird in 1873.The Brooklyn Bridge was under construction from 1870 until 1883.
A permanent European presence in new Netherland began in 1624 with the founding of a settlement in the island of the Governors of the Dutch fur trade.In 1625 construction began on a Citadel and a Fort Amsterdam on Manhattan island, later called new Amsterdam (Nieuw Amsterdam).Manhattan island was chosen as the site of Fort Amsterdam, a Citadel for the protection of the newcomers;its 1625 establishment is recognized as the date of birth of the city of New York.According to the document by Pieter Janszoon Schagen our people (ons Volck) - Peter Minuit is not explicitly mentioned there - Manhattan purchased in 1626 of Lenape native American peoples in exchange for goods worth 60 guilders, it is often said that worth $24, though (comparing the price of bread and other products) really equivalent to around $ 1000 in modern currency (the calculation by the International Institute of Social History Amsterdam).
In 1647, Peter Stuyvesant was appointed as the last Dutch Director-General of the colony.New Amsterdam was formally incorporated as a city in 02 February 1653.In 1664, the English conquered new Netherland and renamed "New York" after the English Duke of York and Albany, the future King James II.Stuyvesant and his Council negotiated with the British to produce 24 articles of provisional transfer intended to guarantee new Netherlanders liberties, including freedom of religion, under the Spanish domain.
The Dutch Republic regained it in August 1673 with a fleet of 21 ships, they changed the name of the city to "New Amsterdam".New Netherland was ceded permanently to the English in 1674 November via the Treaty of Westminster, in exchange for the island that was the last long link of the nutmeg coveted Dutch trading monopoly in Indonesia.
American Revolution and the first United States
Prelude to colonial opposition organized to the British Empire, the representatives of all the thirteen colonies stamp Act Congress was held in New York in 1765.The Congress gave rise to the Declaration of rights and grievances, the first document by a body representing several colonies to affirm the concept popularly known as "no taxation without representation".Also was the first time colonies cooperated to a political objective unified and they laid the groundwork for the Continental Congress that followed years later.
Sons of Liberty developed in Manhattan in the days following the protests of the stamp Act.Participated in a long-term confrontation with British authorities on the poles of freedom that were alternately raised by the sons of liberty and cut by the British authorities.The skirmishes ended when the New York Provincial Congress revolutionary took power in 1775.

Construction of the Manhattan Bridge.

Substrate of much of Manhattan is a mica known as Manhattan schist schist.Is a strong metamorphic rock, competent adapted well to the foundations of tall buildings and the two large concentrations of skyscrapers on the island occur in places where the formation is near the surface.In Central Park, there are outcrops of schist of Manhattan and Rock rat is a large enough sample.
Geologically, a predominant substrates of Manhattan feature is that the underlying foundation of the rock of the island rises considerably closer to the surface near the District of midtown, dips down under between 29th Street and Canal Street, then rises to the surface again under the financial district.This is the rationale of the grouping of skyscrapers in the areas of financial and Midtown district and its absence on the intermediate territory between these two areas, since its foundations can be sunk more firmly on solid foundations.
A consequence of the strict plan of the grid in most of Manhattan and bias of the grid of 28.9 degrees, is a phenomenon known as Manhattanhenge (by analogy with Stonehenge).On separate occasions in late May and early July, the sunset is aligned with grid lines of street, with the result that the Sun is visible at or near the Western horizon from street level.A similar phenomenon occurs with the sunrise in January and December.
At a glance facing north from The Empire State Building
Manhattan was at the heart of the campaign of New York, a series of major battles in the early American Revolutionary War.The Continental Army was forced to abandon Manhattan after the disastrous battle of Fort Washington on 16 November 1776.The city became the British political and military Center of operations in North America for the remainder of the war.Manhattan suffered greatly by the great fire of New York during British military rule that followed.British occupation lasted until November 25, 1783, when George Washington returned to Manhattan, as the last British forces left the city.
Since January 11, 1785 to the fall of 1788, New York City was the fifth of five capitals under the articles of Confederation, with the meeting of the Continental Congress in the Hall of the city of New York (then at Fraunces Tavern).New York was the first capital under the newly enacted Constitution of the United States, from March 04, 1789 to August 12, 1790 at Federal Hall.The Supreme Court of United States sat for the first time, the Charter of rights of United States were drawn up and ratified, and the first steps of adding States to the Union with the approval of the Northwest Ordinance all took place there.
Crecimiento del siglo XIX
Nueva York creció como un centro económico, primero como resultado de las políticas y prácticas como el primer Secretario del Tesoro Alexander Hamilton y, después, con la apertura del Canal Erie en 1825, que conecta el Puerto Atlántico con los vastos mercados agrícolas del medio oeste de Estados Unidos y Canadá.
Tammany Hall, una máquina política del Partido Demócrata, comenzó a crecer en influencia con el apoyo de muchos de los inmigrantes irlandeses, que culminó en la elección del primer alcalde Tammany, Fernando Wood, en 1854. Tammany Hall dominó la política local por décadas. Central Park, que abrió sus puertas al público en 1858, se convirtió en el primer parque paisajístico de una ciudad estadounidense y primer parque público de la nación.
Durante la Guerra Civil estadounidense, fuertes lazos comerciales de la ciudad con el sur de Estados Unidos, su creciente población inmigrante (antes entonces en gran parte de Alemania e Irlanda), ira sobre servicio militar obligatorio y el resentimiento a quienes podía permitirse pagar $300 para evitar el servicio, llevaron al resentimiento contra las políticas de guerra de Lincoln, que culminó en los tres días largos Nueva York proyecto disturbios de julio de 1863uno de los peores incidentes de desorden civil en la historia estadounidense, con un estimado 119 participantes y transeúntes masacrados.
The rate of immigration from Europe grew steeply after the Civil war and New York became the first stop for millions seeking a new and better life in the United States, a role recognized by the dedication of the statue of liberty on October 28, 1886, a gift from the people of France.The new European immigration brought further social upheaval.In a city of tenements packed with poorly paid workers in dozens of Nations, the city was a hotbed of revolution, syndicalism, blackmail and unionization.
In 1883, the opening of the Brooklyn Bridge had established a connection of road along the East River.In 1874, the western part of the present Bronx County was transferred to New York County, and in 1895 was annexed the rest of the current County of Bronx.The greater New York City was founded in 1898, when four counties consolidated to form one city of five boroughs.Manhattan and the Bronx, though still one County, established as two separate districts.01 January 1914, the New York State legislature created Bronx County and New York County was reduced to its present boundaries.
The 20th century

The newly completed Singer Building dominating over the city, 1909
The construction of New York City subway, opened in 1904, helped unite the city, as did additional bridges to Brooklyn.In the 1920s, Manhattan saw large arrivals of African-Americans as part of the great migration from the South of United States and the Harlem Renaissance, part of a longer boom at the time of the ban that included new skyscrapers that compete for the horizon.New York City became the largest city in the world in 1925, overtaking London, which had reigned for a century.
On March 25, 1911, the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory in Greenwich Village fire killed 146 garment workers dress.The disaster led to revisions of the Fire Department of the city, building codes and regulations of work.
The period between the world wars saw the election of reformist Mayor Fiorello La Guardia and the fall of Tammany Hall after 80 years of political domination.Stabilization of the demographics of the city, organise work brought new protections and wealth to the working class, the Government of the city and infrastructure underwent a dramatic revision under La Guardia.Despite the great depression, some of the world's tallest skyscrapers were completed in Manhattan during the early 1930s, including numerous masterpieces of Art Deco still forming part of the skyline of the city today, including the Empire State building, the Chrysler Building and the GE building.
Returning World War II veterans created a postwar economic boom, which led to the development of large housing developments aimed at returning veterans, including Peter Cooper Village-Stuyvesant Town, which opened in 1947.In 1951, the UN moved from its first headquarters in Queens, on the East Side of Manhattan.
As many major cities of United States, New York suffered race riots and population and industrial decline in the 1960s.In the 1970s, the city had gained a reputation as a relic covered with graffiti, mounted by the crime in history.In 1975, the Government of the city before the imminent bankruptcy, and its appeals for assistance were initially rejected, summarized by the classic October 30, 1975 holder of the New York Daily News as "Ford to city: Drop Dead".The fate was avoided through a federal loan and debt restructuring, and the city was forced to accept increased financial scrutiny by the State of New York.
The 1980s saw a rebirth of Wall Street, and the city claiming its role at the center of the financial industry around the world.The late 1980s also saw Manhattan in the heart of the AIDS crisis, with Greenwich Village in its epicenter.Gay Men Health Crisis (GMHC) and coalition of AIDS to be able to give free rein (ACT UP) were founded to advocate on behalf of those affected with the disease.Most populous ethnic Manhattan, white, group decreased from 83.5% in 1940 to 58.3 per cent in 1990.
From the 1990s, crime rates fell dramatically, with homicide rates that had reached 2,245 in 1990 fell to 537 in 2008, and the epidemic of crack and violence related to drugs associated under more control.Turned the exit of the population, as the City returned to be the destination of immigrants from all over the world, together with low interest rates and Wall Street bonuses to feed the growth of the real estate market.
Manhattan 1609 vs. 2012: wonder nature to the urban jungle
Before it was an urban jungle, Manhattan was home to the native Lenape, who called the island Mannahatta, or "land of many hills."
Built up and - thanks to the recovery of land-, Center of Manhattan, circa 2008, towers on the island of the city of New York as it was more than 400 years ago (to the right computer processing), when Europeans initially eyes — with bonfires.
Images were created for the project of Mannahatta's Wildlife Conservation Society, released April 20 and includes a book, the museum exhibit and Web site.The celebration of a year of natural history in Manhattan seeks to recreate the island as it seemed 400 years ago, English Explorer of the day which came from Henry Hudson in 1609.
— Image courtesy Markley Boyer, Mannahatta Project/Wildlife Conservation Society
Built partly on reclaimed land, the neighborhood of Battery Park City (left) anchors the Western side of the southern end of modern Manhattan, whose coast is considerably extended since 1609.
As in Manhattan today, part of the charm of Mannahatta their neighborhoods, said Eric Sanderson, leader of the Mannahatta project, which began on April 20, 2009.But the enclaves of Mannahatta were defined by their unique communities of plants and animals, such as wolves, pumas, moose, deer and Beaver.
"There were 55 different ecological communities", Sanderson estimated.Acre by acre, 'is more ecological communities... that most of the national parks'.
— Image courtesy Markley Boyer, Mannahatta Project/Wildlife Conservation Society
In 1609 a large settlement of Lenape Indians called eastern foot of Inwood Hill House (see campfires in the illustration to the right), as does the neighborhood Inwood. todayThe site offers convenient access from the Indians to the Harlem River (left) and the Hudson River, home to rich fishing.
Inwood Hill Park contains the last natural forest and marshes in Manhattan.
"Legend has it that there was a tree in the park where Peter Minuit [a colonial administrator of the Dutch East India Company] bought the island from the Indians in 1626]," said Eric Sanderson, head of the Mannahatta project, which began on April 20, 2009."Is supposed to they have been shot down in 1926".
— Image courtesy Markley Boyer, Mannahatta Project/Wildlife Conservation Society
Four hundred years of Manhattan Upper East Side (front left) and neighborhoods of Harlem (left background) were territories of hunting and gathering Indian Lenape (illustration, right).
Mannahatta Project director Eric Sanderson hopes that knowledge of the past of Manhattan help urban planners to build better cities tomorrow.
Has an experiment for them: "If you knew all about original ecology of Mannahatta and could rebuild Manhattan using the best ideas of green design today, what kind of city will build? "" And what would live there?"
— Image courtesy Markley Boyer, Mannahatta Project/Wildlife Conservation Society
Geography

Central Park is visible in the center of this satellite image.Manhattan is bound by the Hudson River to the West, the Harlem River to the North and the East River to the East.
Substrate of much of Manhattan is a mica known as Manhattan schist schist.Is a strong metamorphic rock, competent adapted well to the foundations of tall buildings and the two large concentrations of skyscrapers on the island occur in places where the formation is near the surface.In Central Park, there are outcrops of schist of Manhattan and Rock rat is a large enough sample.
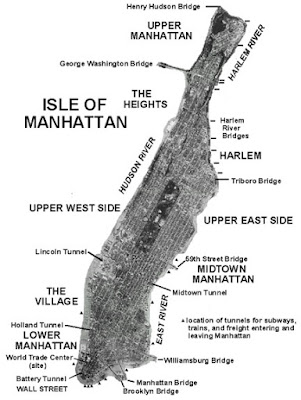
Manhattan is divided into Centre (Lower Manhattan), Midtown (Midtown Manhattan) and Uptown (high Manhattan), Manhattan Division sides East and West of Fifth Avenue.Manhattan island is bounded by the Hudson River to the West and the East River to the East.To the North, the Harlem River divides the island of Manhattan from the Bronx and the United States.Several small islands are also part of the Borough of Manhattan, including Randall Island, island rooms and Roosevelt Island in the East River, and Governors Island and liberty in New York Harbor South Island.Manhattan island is 22.7 square miles (59) in the area, 13.4 miles (21.6 km) long and 2.3 miles (3.7 km) wide, at its widest (near 14th Street).The County of New York in its entirety covers a total area of 33.77 square miles (87.5 km2), of which 22.96 square kilometers (59.5) are land and 10.81 square miles (28.0) is water.
A neighborhood of the New York County is contiguous with the Bronx.Marble Hill at one time was part of Manhattan island, but the Harlem River Ship Canal, dug in 1895 to improve navigation on the Harlem River, separated from the rest of Manhattan as an island between the Bronx and the rest of Manhattan.Before of World War I, the section of the canal is filled original Harlem River separates the Bronx Marble Hill and Marble Hill became part of the continent.
Marble Hill is an example of how the land of Manhattan has been altered considerably by human intervention.District has seen substantial land reclamation along its banks from the Dutch colonial era, and much of the natural variation in topography has been standardized.
In the nineteenth century, landfill was used to expand Lower Manhattan from the coast of natural Hudson on Greenwich Street in the West of the street.When the World Trade Center, 1.2 million cubic yards (917.000 m³) of material was excavated from the site.Instead of dumping the spoil at sea or in landfills, the fill material was used to expand the coast of Manhattan on West Street, Battery Park City building.The result was an extension of 700 feet (210 m) into the River, with six blocks or 1,484 feet (450 m), covering 92 acres (37 hectares), providing a 1.2 mile (1.9 km) concourse from the edge of the river and more than 30 acres (12 hectares) of parks.
A modern redefinition of the version of 1807 of the Commissioner for Manhattan grid plan, a few years earlier that was adopted in 1811.Central Park is absent.
Geologically, a predominant substrates of Manhattan feature is that the underlying foundation of the rock of the island rises considerably closer to the surface near the District of midtown, dips down under between 29th Street and Canal Street, then rises to the surface again under the financial district.This is the rationale of the grouping of skyscrapers in the areas of financial and Midtown district and its absence on the intermediate territory between these two areas, since its foundations can be sunk more firmly on solid foundations.
Manhattan has set up connections with New Jersey Highway, to the West by the George Washington Bridge, Holland Tunnel and Lincoln Tunnel and three of the four other boroughs of New York City - the Bronx to the Northeast and Brooklyn and Queens on Long Island to the East and South.Its only direct connection with the fifth district of the city of New York is the Staten Island Ferry in the port of New York, which is free of charge.The ferry terminal is located near Battery Park at its southern end.Is possible to travel overland to Staten Island by way of Brooklyn, using the Verrazano-Narrows Bridge.
Plan of Commissioners of 1811, called for twelve numbered avenues North and South roughly parallel to the shore of the Hudson River, each 100 feet (30 m) wide, first Avenue on the East side and twelfth Avenue in the West.There are several intermittent avenues East of First Avenue, including four additional lettered avenues running from Avenue an eastward to Avenue D in an area now known as Alphabet City in the East Village of Manhattan.The numbered streets of Manhattan east-west and are 60 feet (18 m) in width, with close to 200 feet (61 m) between each pair of streets to.With each combined Street and block adding up to about 260 feet (79 m), there are almost exactly 20 blocks per mile.The typical block in Manhattan is 250 for 600 feet (180 m).
According to the original Plan of the Commissioner there were 155 numbered crosstown streets, but later the grid has been extended to the corner more to North of Manhattan, where the last numbered Street is 220th Street (Manhattan).In addition, the numbering system continues even in the Bronx, North of Manhattan, while the plan of the network is not so regular;there is the last numbered Street 263rd Street.
Fifteen crosstown streets were designated as 100 feet (30 m) wide, including 34, 42, 57 and 125 streets, some transport more important of the municipality and businesses.Broadway is the most notable of many exceptions to the network, starting at Bowling Green in lower Manhattan and continuing North to the Bronx at the northern tip of Manhattan.In much of Midtown Manhattan, Broadway runs at a diagonal to the grid, creating intersections named major Madison Square (Fifth Avenue and 23rd Street), Herald Square (Sixth Avenue and 34th Street), Times Square (Seventh Avenue and 42nd Street), Union Square (14th Street and Park Avenue South/Fourth Avenue), Columbus Circle (Eighth Avenue and Central Park West and 59th Street).
 |
| Times Squarea place cultural important in the city |
The Wildlife Conservation Society, which operates the zoos and aquariums in the city, is undergoing the Mannahatta, a computer simulation project visually reconstruct the ecology and geography of Manhattan when Henry Hudson first sailed by in 1609, and compare it to what we know of the island today.
Click on the image to enlarge

Panorama of Midtown Manhattan, as seen from the observation deck of the GE building
Picture of Upper Manhattan and Midtown Manhattan from Jersey City
Manhattan Island