Lumbar arthritis
Lumbar arthritis
- Introduction
- What are the lumbar vertebrae?
- What is low back pain?
- What are the causes of low-back pain?
- What symptoms you are experiencing and lumbar osteoarthritis is diagnosed?
- What factors influence the appearance of lumbar osteoarthritis?
- How is the lumbar osteoarthritis treated?
INTRODUCTION
Lumbar arthritis is without a doubt one of the most important causes of pain in the lumbar region, because of its high frequency in the population. It is estimated that more than 80% of people have suffered an episode of low back pain at some point in their lives. Up to 30% of the total pension for incapacity for work are for the lumbar spine problems.WHAT ARE THE LUMBAR VERTEBRAE?
Within the vertebral column as a whole, the lumbar spine consists of 5 vertebrae located in the back, between the dorsal or chest region as the upper limit and the region of the pelvis as the lower limit. He is what is popularly known as 'kidney zone'.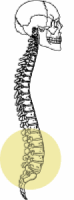
The lumbar spine, the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, form a flexible anatomical structure that allows that we can make movements of flexion or extension of the trunk or turn of the vehicle movements. Due to this ability to move and that, on many occasions, this part of the column is often subject to some very important mechanical overload (for example when we load heavy objects or maintain positions forced in a prolonged way) the lumbar region is the cause of painful symptoms.
WHAT IS LOW BACK PAIN?
Referred to as low back pain or lumbago to all pain appearing in the lumbar spinal region or in the proximal muscles related to this part of the column. When this pain in the lumbar region extends by the lower limbs, in general beyond the knee, we speak of the existence of a sciatica or lumbo sciatica.In the medical field, there is a distinction between acute low back pain and chronic low back pain. Mark the difference between the time of duration of the pain. In general, it is said that a patient has a chronic back pain when the duration of the pain exceeds 6 weeks. Acute lumbago are episodes of LBP self-limiting and more cut in time.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF LOW-BACK PAIN?
Possible causes of back pain are numerous, lumbar osteoarthritis to be one of the most frequent. However, may occur low back pain due to other problems such as muscle contractures, Herniated discs, inflammation or injury in the vertebrae, etc. For this reason it is very important that, before any back pain, consult with your doctor, to reach an accurate diagnosis and, on the basis of this diagnosis, to establish appropriate treatment.On many occasions, despite appropriate medical evaluation, it is not possible to arrive at a definite diagnosis. It is what is called "non-specific low back pain", process that, fortunately, is benign and generally good prognosis.

WHAT SYMPTOMS HAS AND AS LUMABAR OSTEOARTHRITIS IS DIAGNOSED?
As in osteoarthritis from other locations, in the lumbar spine arthritis is manifested with pain and limitation of the movements of the lumbar spine. The characteristics of these symptoms are referred to as "mechanical pain"; that is, they pertain, and increase with the movements and physical overload, better with rest and immobility.Lumbar arthritis is easily diagnosed through assessment of symptoms and physical examination the doctor performing the patient. The study is completed and the diagnosis is confirmed with the realization of radiographs of the lumbar spine, in which the doctor can objectify typical radiologic changes of osteoarthritis.
Other more sophisticated and complex, as the scanner diagnostic testing and magnetic resonance imaging, are not necessary to diagnose lumbar arthritis. The physician only tells them when some complication associated with arthritis is suspected, or if you were to consider a surgical solution (operation) for the patient lumbar problem.
WOULD WHAT FACTORS INFLUENCE THE APPEARANCE OF LUMBAR OSTEOARTHRITIS?
The lumbar spine has a key role in the support of the weight and the burden of the entire trunk and head, and it is shown that obesity, postural defects to sit, bad habits to sleep, charge weights, improper turns, etc., if they are severe or prolonged, adversely affect lumbar osteoarthritis symptoms or progression of the same.Knowledge of these factors is fundamental to try to correct them, which constitutes an important measure of prevention of lumbar osteoarthritis. In addition, in patients who already have it, your correction is associated with a better outcome of osteoarthritis.
HOW LUMBAR OSTEOARTHRITIS TREATED?
Once the doctor has diagnosed a lumbar osteoarthritis, it will instruct the patient a series of measures and, occasionally, drug treatment, that are aimed at two main goals: pain relief and the maintenance of the function of the lumbar spine.In general, rest is only a temporary measure indicated in periods of intensity of pain. Its duration generally should not exceed 3 or 4 days.
Drugs such as painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, sometimes associated with relaxing muscle are used for the treatment of pain.
Other therapeutic measures, such as physical therapy or rehabilitation treatment, constitute an effective tool in the improvement of pain and functional recovery of the spinal column. In the treatment of osteoarthritis other drugs aimed at reducing progression of the same are used occasionally. The doctor, individually assessing each patient, is in charge of indicate this type of modifier medication in the course of the disease.
It is important that patients diagnosed with lumbar osteoarthritis will attend what is called back schools. In them patients are trained, in individual or collective form, in the performance of daily activities, avoiding the circumstances that increase the pain, treating that patient can return to his usual physical and occupational activity. Back school the patient receives a teaching about the mechanisms by which low-back pain occurs, and learn how to correct postures or inappropriate attitudes in activities such as work, the way of sitting, Crouching, sleep, etc. Also, learn how to perform a series of physical exercises aimed at improving symptoms suffering, preventing the progression of osteoarthritis.
